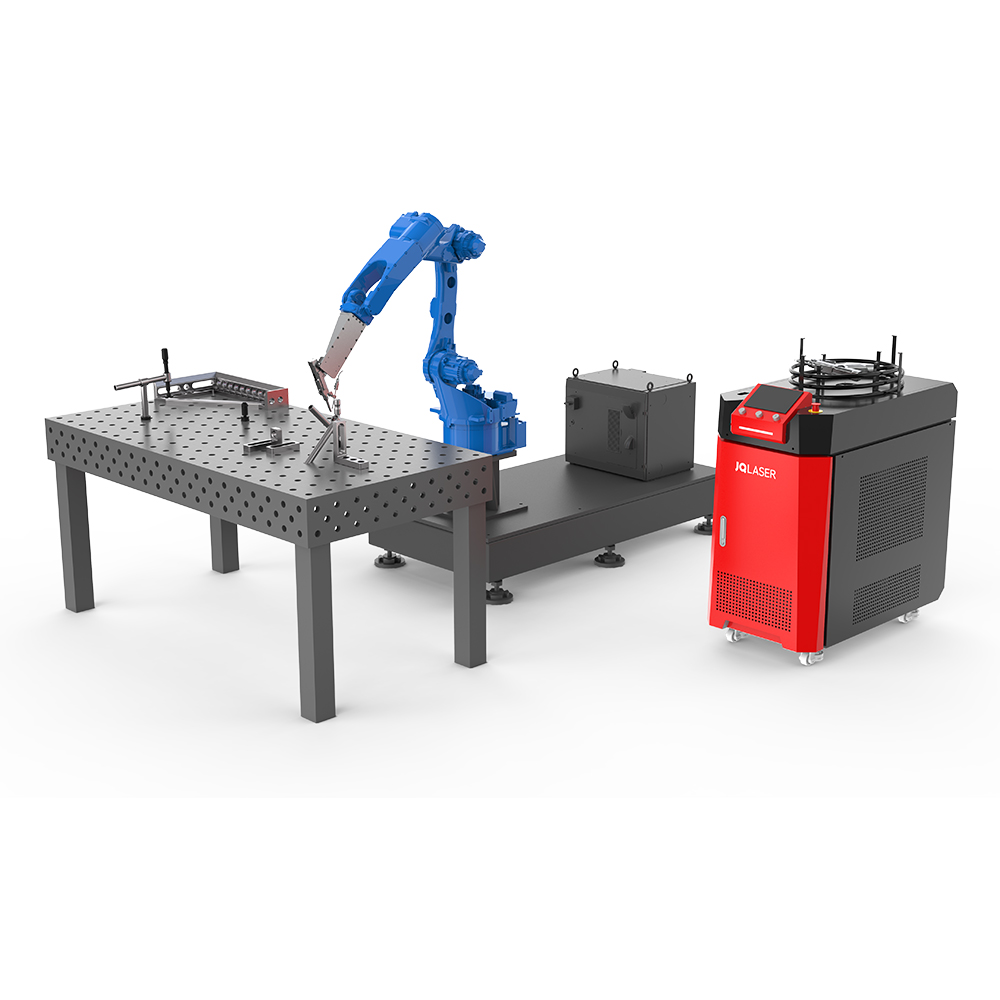
Effect of welding parameters on surface formation of welded joints
The laser welding parameters of stainless steel sheets are shown in the table. In the aluminum-nickel laser welding test, the welding parameters involved mainly include laser frequency, laser power and welding speed. Because they have different effects on the joint, the degree of impact on the performance of the joint is also different. Through literature review and some experimental research, it is found that when the laser frequency is 200Hz, the welding effect is best and can ensure a small heat input.
| No. | Laser power/kW | Welding speed/mm/s | Laser frequency/Hz |
| 1 | 1.8 | 40 | 200 |
| 2 | 2.0 | 40 | 200 |
| 3 | 2.4 | 40 | 200 |
| 4 | 2.6 | 40 | 200 |
| 5 | 2.2 | 0 | 200 |
| 6 | 2.2 | 30 | 200 |
| 7 | 2.2 | 20 | 200 |
| 8 | 2.2 | 40 | 200 |
Effect of laser power on surface formation of welded joints
When the laser power is small, the overall deformation of the welded specimen is small, there are no obvious defects such as pores and cracks on the weld surface, there are no obvious spatters and undercuts, and there is a corrugated texture. When the welding speed remains unchanged, as the laser power increases, the melting width of the front side of the weld increases. When the laser power is <1.8kW, there is an obvious depression in the center of the weld, and the oxidation phenomenon is not obvious; when the laser power is 2.0kW, the weld is well formed, and the oxidation phenomenon is not obvious; when the laser power is 2.2kW, the weld is formed Good, the surface is smooth and beautiful, and the texture is clear; when the laser power is 2.4kW, the weld is well formed, the surface is oxidized more seriously, and the back side is just welded through; when the laser power is 2.6kW, the weld is completely welded through, and the molten pool metal When rolled up, it appears black and oxidized very seriously.



Effect of welding speed on surface formation of welded joints
There are no obvious defects such as pores and cracks on the surface of the weld. The overall deformation of the welded specimen is small, there is no obvious spatter and undercut, and there is a corrugated texture. When the laser power remains constant, as the welding speed slows down, the width of the weld shows an increasing trend; when the welding speed is 50mm/s, the joint melting width is small and there is a linear depression in the center of the weld; when the welding speed When the speed is 40mm/s, the weld is fully penetrated and well formed, with a smooth and beautiful surface and clear texture; when the welding speed is 30mm/s, the weld width is large and the surface is seriously oxidized; when the welding speed is 20mm/s, The weld seam was severely oxidized and began to undergo significant deformation. The weld seam was distorted and the back side was welded through.



Effect of laser welding parameters on penetration depth and width
The welding quality of the aluminum-nickel lap welded structure not only depends on the mechanical properties of the joint, but is also related to the weld formation and the degree of oxidation and discoloration. Weld penetration depth and width are important factors to measure the surface formation of the joint, the degree of oxidation and discoloration on the back side, and the mechanical properties. The penetration depth mainly affects the quality of the backside of the joint weld, while the penetration width mainly affects the mechanical properties of the joint. Laser welding parameters (laser power, welding speed) are important factors affecting welding quality.
Effect of laser power on melting depth and melting width
The penetration depth and width of the weld are greatly affected by the laser power, while the reinforcement of the weld does not show regularity. The reason for the larger reinforcement under some parameters may be caused by the direction of the shielding gas. When the laser power is small (1.8kW), the stainless steel sheet is only slightly melted, and the weld penetration depth and width are narrow. As the laser power increases, the penetration depth and width increase significantly. When the laser power reaches 2.4kW, the weld is just penetrated. As the laser power increases again, the penetration width continues to increase, and the back weld also becomes Then widen.
Effect of welding speed on penetration depth and width
As the welding speed decreases, the penetration depth and width increase significantly. When the welding speed is only 30mm/s, the weld will be completely penetrated. As the laser power increases again, the penetration width continues to increase, while the back welding The seam is also melted and widened.
Conclusion
1) When the power increases, the laser heat input increases, the melting amount of the metal material to be welded will increase, and the size of the molten pool will increase accordingly, thereby increasing the weld width. The faster the welding speed, the faster the laser beam moves on the surface of the test piece, the energy input into the weld per unit time and unit length decreases, the laser welding heat input decreases, and the melting amount of the welded metal material decreases, thus making The weld width becomes smaller.
2) In aluminum-nickel laser welding joints, when the laser power is low or the welding speed is high, the base metal melting amount at the aluminum-nickel joint interface is smaller, and the melting width and deformation of the aluminum-nickel joint are smaller; when When the laser power increases or the welding speed decreases, the melting amount of the base metal increases and the melting width of the weld increases.