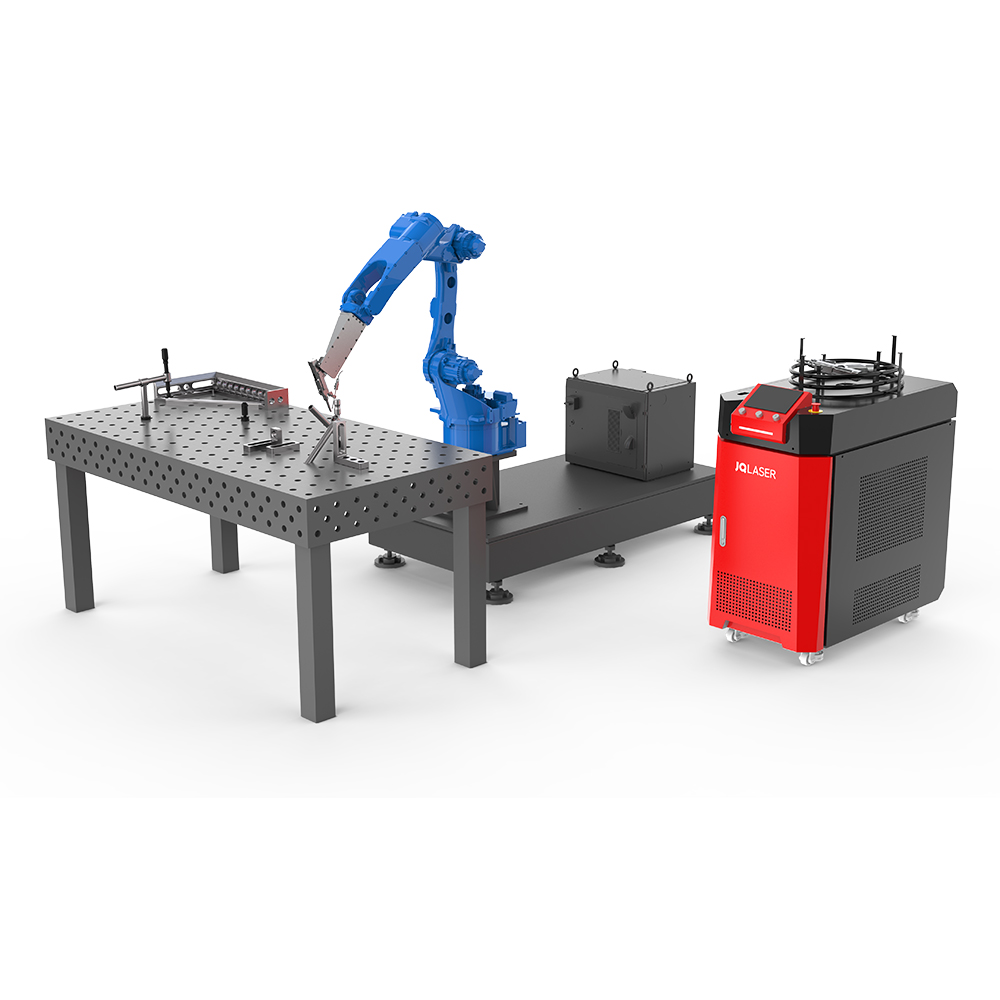
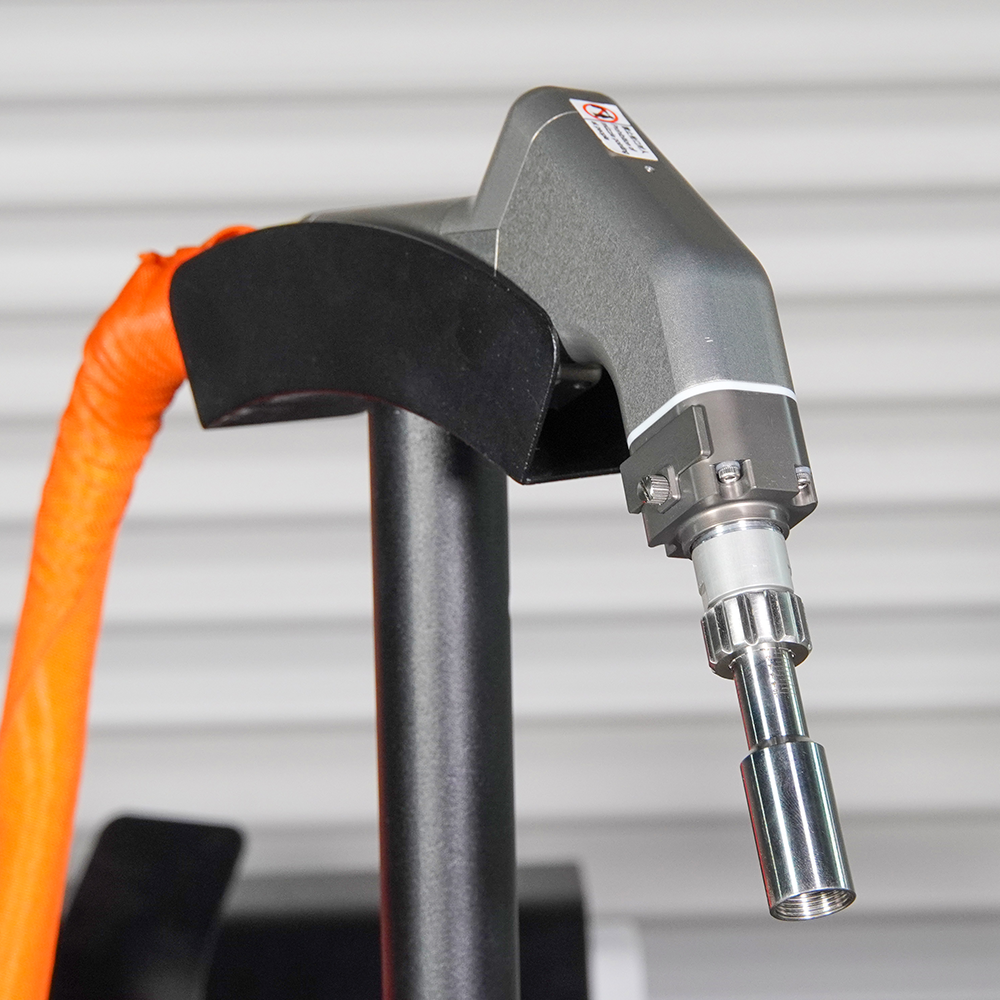
Introduction
In the realm of modern manufacturing and engineering, precision and efficiency are paramount. Traditional welding techniques have been widely used for joining materials, but they often come with limitations such as heat distortion, porosity, and imprecise welds. However, with the advent of laser welding machines, a revolutionary technology has emerged that addresses these issues and unlocks the potential of precision joining.
Understanding Laser Welding Machines
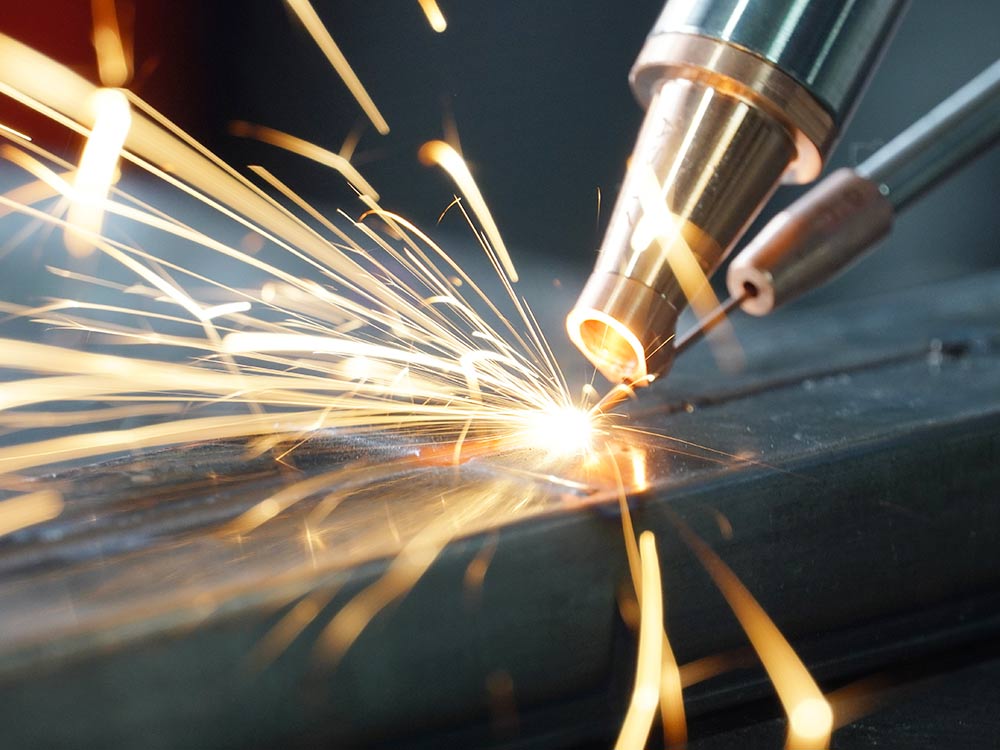

2.1 What is Laser Welding?
Laser welding is a non-contact joining process that utilizes a highly focused laser beam to melt and fuse materials together. The intense energy delivered by the laser creates a localized weld seam, resulting in minimal heat diffusion to the surrounding areas. This characteristic makes laser welding ideal for working with delicate and intricate components.
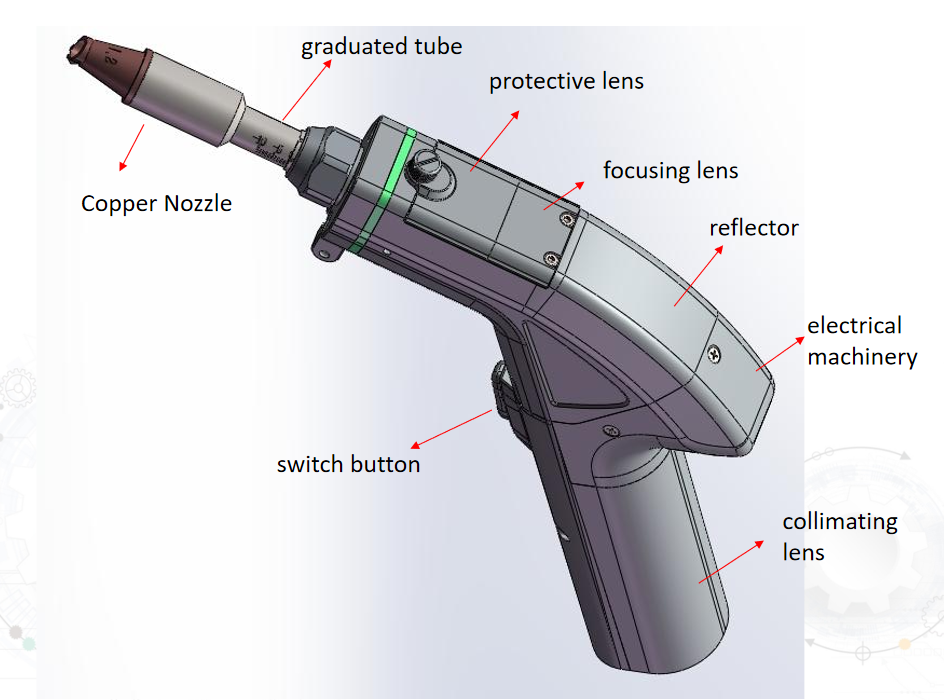
2.2 How Laser Welding Machines Work
Laser welding machines consist of a laser source, beam delivery system, and a workpiece holding mechanism. The laser source generates the high-intensity beam, which is then transmitted through optical fibers or mirrors to the workpiece. The focused laser beam strikes the material, causing it to melt, and upon cooling, a strong and precise bond is formed.
Advantages of Laser Welding Machines
3.1 Precision Joining
One of the most significant advantages of laser welding machines is their ability to achieve exceptional precision in joining materials. The focused laser beam allows for pinpoint accuracy, enabling intricate welding tasks with minimal distortion or damage to the surrounding areas.
3.2 Versatility in Materials
Laser welding machines can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and even dissimilar materials. This versatility makes them indispensable in various industries that require the joining of different materials for their products.
3.3 Non-Contact Welding
Unlike conventional welding methods that require direct contact with the workpiece, laser welding is a non-contact process. This feature eliminates the need for physical force during welding, minimizing the risk of contamination and reducing wear and tear on the equipment.
3.4 Minimal Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
The controlled and focused nature of laser welding results in a smaller heat affected zone (HAZ). This reduced HAZ prevents material warping and distortion, making laser-welded components structurally sound and aesthetically pleasing.
Applications of Laser Welding Machines

4.1 Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, precision and durability are vital for safety and performance. Laser welding machines are extensively used for joining components like gears, engine parts, and body panels with unmatched accuracy and strength.
4.2 Aerospace Applications
Aerospace engineering demands lightweight and robust components. Laser welding facilitates the production of aircraft parts, ensuring reliable connections without compromising structural integrity.
4.3 Electronics and Semiconductors
The electronics industry requires delicate welding processes. Laser welding machines can work with miniature components, such as microchips and sensors, enabling seamless connections in intricate devices.
4.4 Medical Devices
Laser welding has revolutionized the medical device industry by allowing the fabrication of precise and biocompatible instruments, implants, and surgical tools.
4.5 Jewelry and Fashion Industry
Artistry meets precision with laser welding machines in the jewelry and fashion industry. Delicate and intricate designs can be seamlessly joined with minimal risk of damage to precious materials.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Laser Welding Machine
5.1 Power and Energy Density
The power output and energy density of the laser welding machine must match the specific requirements of the materials and applications to achieve optimal results.
5.2 Beam Quality and Focusability
High beam quality ensures a focused and intense laser beam, crucial for achieving precision and accuracy in welding.
5.3 Pulse Duration
The pulse duration determines the amount of energy delivered to the workpiece. Short pulses are ideal for delicate materials, while longer pulses are suitable for thicker ones.
5.4 Cooling System
Efficient cooling systems are necessary to maintain the laser source and optical components at optimal temperatures during prolonged welding operations.
5.5 Automation and Integration Capabilities
For streamlined production processes, consider laser welding machines that offer automation and integration features, enabling seamless workflow management.
Best Practices for Laser Welding
6.1 Surface Preparation
Proper surface preparation is crucial for successful laser welding. Clean and properly aligned surfaces ensure the best welding results.
6.2 Choosing the Right Parameters
Understanding the material properties and adjusting welding parameters accordingly is essential to achieve the desired weld quality.
6.3 Quality Control and Testing
Regular quality control checks and testing during and after welding help identify any defects and ensure consistent weld quality.
Overcoming Challenges in Laser Welding
7.1 Welding Thick Materials
Laser welding thick materials requires adjusting the laser parameters to provide sufficient energy for complete penetration.
7.2 Joining Dissimilar Materials
Special considerations must be taken into account when welding dissimilar materials due to their differing thermal properties.
7.3 Managing Heat and Distortion
Implementing proper cooling and heat management techniques can prevent material distortion during the welding process.
The Future of Laser Welding Machines
8.1 Advancements in Fiber Laser Technology
Fiber laser technology continues to evolve, providing higher power and improved beam quality, further enhancing the capabilities of laser welding machines.
8.2 Integration with Industry 4.0
The integration of laser welding machines with Industry 4.0 technologies will lead to enhanced automation, real-time monitoring, and data-driven process optimization.
Conclusion
Laser welding machines have revolutionized the precision joining landscape in various industries. Their ability to deliver exceptional accuracy, versatility, and non-contact welding has unlocked new possibilities in manufacturing and engineering. As advancements in technology continue, the future of laser welding machines looks even more promising, solidifying their position as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing.
FAQs
- Q: Are laser welding machines suitable for delicate materials like electronics and medical devices?A: Yes, laser welding machines are well-suited for delicate materials due to their non-contact nature and ability to provide precise welds.
- Q: What materials can be welded using laser welding machines?A: Laser welding machines can work with a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and even dissimilar materials.
- Q: Can laser welding machines be automated for mass production?A: Yes, many laser welding machines offer automation and integration capabilities for streamlined mass production processes.
- Q: How can I ensure the quality of laser-welded components?A: Regular quality control checks and testing during and after welding help ensure consistent weld quality.
- Q: What advancements can we expect in laser welding technology?A: The future of laser welding machines will see advancements in fiber laser technology, providing higher power and improved beam quality, as well as integration with Industry 4.0 technologies for enhanced automation and optimization.